Rare-earth magnets NdFeB (neodymium-iron-borron) are currently the strongest permanent magnets. The original material is produced by sintering and then cut to resulting shapes in accordance with the dimensional requirements of the customer. Thanks to this production process, it is possible to supply a wide range of various shapes.
Rare-earth magnets NdFeB (neodymium-iron-borron) are currently the strongest permanent magnets. The original material is produced by sintering and then cut to resulting shapes in accordance with the dimensional requirements of the customer. Thanks to this production process, it is possible to supply a wide range of various shapes.
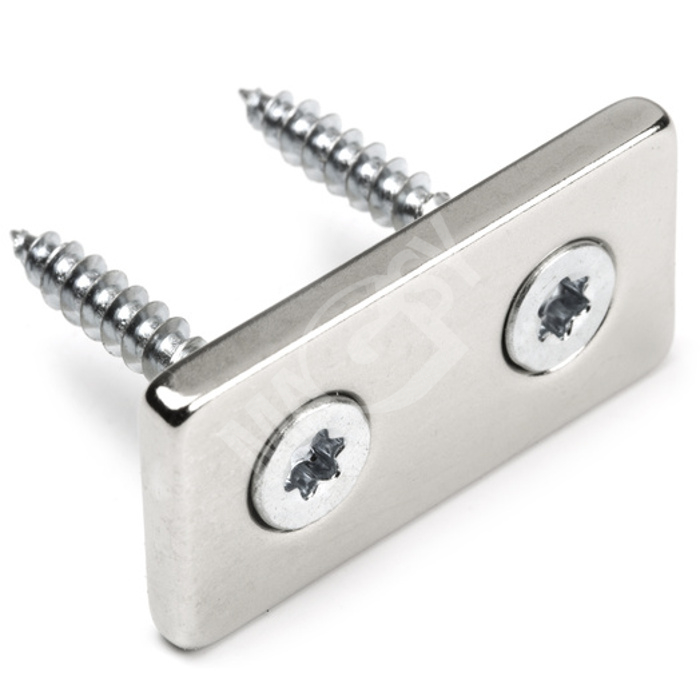 We broadened our offer of neodymium magnets with new articles. These are magnets including a screw hole (countersunk-head bolt), in cubic and cylindrical shapes. The magnets may be screwed onto non-metallic surfaces.
We broadened our offer of neodymium magnets with new articles. These are magnets including a screw hole (countersunk-head bolt), in cubic and cylindrical shapes. The magnets may be screwed onto non-metallic surfaces.
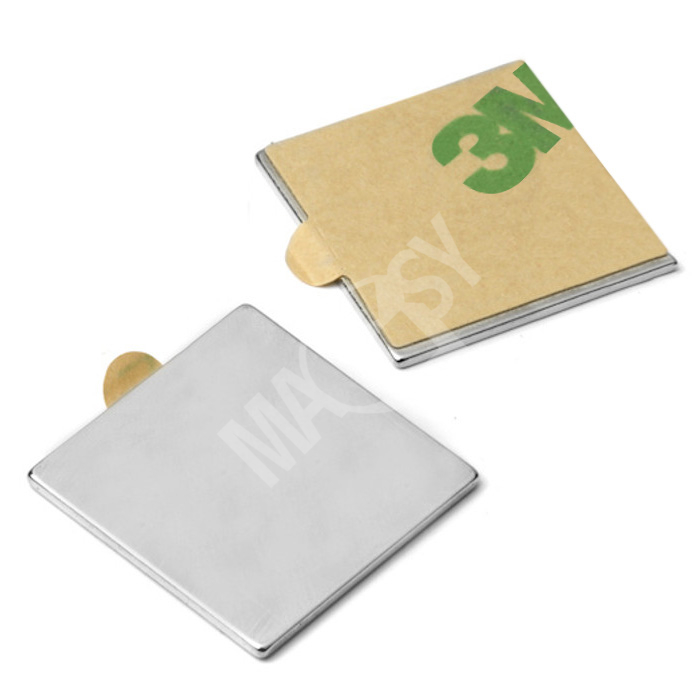 As another choice, magnets with self-adhesive labels, also in cubic and cylindrical shapes, are considered. These magnets are to be simply stuck onto non-metallic surfaces. Due to a strong 3M self-adhesive layer, they hold firmly. We offer these magnets also as pairs where the surfaces without the self-adhesive label attract to each other.
As another choice, magnets with self-adhesive labels, also in cubic and cylindrical shapes, are considered. These magnets are to be simply stuck onto non-metallic surfaces. Due to a strong 3M self-adhesive layer, they hold firmly. We offer these magnets also as pairs where the surfaces without the self-adhesive label attract to each other.
On-line sale of rare-earth NdFeB magnets
Choose the magnet shape and the way of magnetizing
We guarantee operative delivery dates
As for the usual offer of prisms, cylinders and rings, we supply within 3-5 days after receipt your order.
Surface treatment of NdFeB magnets
Rare-earth neodymium magnets are very prone to corrosion, therefore, in principle, surface treatment is used in form of nickel plating (10-20 µm), zinc plating (5-10 µm), epoxy resin plating (20-30 µm) or passivation.
Method of using
Magnets made to measure
In case you do not choose any type suitable directly to you in our internet shop, please contact us. We will send you the quotation dealing with a magnet in question.
Magnets comparison table
| Ferrite isotropic |
Ferrite anisotropic | Rare-earth |
SmCo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ||||
| Force | ||||
| Temperature resistance | ||||
| Chemical resistance |
in the table below you can select the magnetic and physical properties of the material from which the magnet should be produced.
The magnetic characteristics of neodymium magnets (tested at 20 °C)
| Type | Residual Induction (Br) | Coercive Force (Hcb) | Intrinsic Coercive Force (Hcj) | Max. Energy Product (BH max) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mT | kGs | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | kJ/m³ | MGOe | |
| VMM - to 80 °C | ||||||||
| VMM5-N38 | 1220-1300 | 12.2-13.0 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM6-N40 | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM7-N42 | 1290-1350 | 12.9-13.5 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 318-350 | 40-44 |
| VMM8-N45 | 1320-1380 | 13.2-13.8 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 334-366 | 42-46 |
| VMM9-N48 | 1370-1430 | 13.7-14.3 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 358-390 | 45-49 |
| VMM10-N50 | 1400-1450 | 14.0-14.5 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=955 | >=12.0 | 374-406 | 47-51 |
| VMM11-N52 | 1420-1480 | 14.2-14.8 | >=836 | >=10.5 | >=876 | >=11.0 | 390-442 | 49-53 |
| VMM12-N54 | 1450-1510 | 14.5-15.1 | >=836 | >=10.5 | >=876 | >=11.0 | 406-438 | 51-55 |
| VMM M - to 100 °C | ||||||||
| VMM3M-N38M | 1220-1300 | 12.2-13.0 | >=915 | >=11.5 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM4M-N40M | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=939 | >=11.8 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM5M-N42M | 1290-1350 | 12.9-13.5 | >=963 | >=12.1 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 318-350 | 40-44 |
| VMM6M-N45M | 1320-1380 | 13.2-13.8 | >=987 | >=12.4 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 334-366 | 42-46 |
| VMM7M-N48M | 1370-1430 | 13.7-14.3 | >=1019 | >=12.8 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 358-390 | 45-49 |
| VMM8M-N50M | 1400-1450 | 14.0-14.5 | >=1043 | >=13.1 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 374-406 | 47-51 |
| VMM9M-N52M | 1420-1480 | 14.2-14.8 | >=1059 | >=13.3 | >=1114 | >=14.0 | 390-442 | 49-53 |
| VMM H - to 120 °C | ||||||||
| VMM4H-N35H | 1170-1240 | 11.7-12.4 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 263-295 | 33-37 |
| VMM5H-N38H | 1220-1300 | 12.2-13.0 | >=915 | >=11.5 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM6H-N40H | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=939 | >=11.8 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM7H-N42H | 1290-1350 | 12.9-13.5 | >=963 | >=12.1 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 318-350 | 40-44 |
| VMM8H-N44H | 1310-1370 | 13.1-13.7 | >=979 | >=12.3 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 326-358 | 41-45 |
| VMM9H-N46H | 1340-1400 | 13.4-14.0 | >=995 | >=12.5 | >=1353 | >=17.0 | 342-374 | 43-47 |
| VMM10H-N48H | 1370-1430 | 13.7-14.3 | >=1011 | >=12.7 | >=1274 | >=16.0 | 358-390 | 45-49 |
| VMM11H-N50H | 1400-1450 | 14.0-14.5 | >=1027 | >=12.9 | >=1274 | >=16.0 | 374-406 | 47-51 |
| VMM SH - to 150 °C | ||||||||
| VMM3SH-N33SH | 1140-1210 | 11.4-12.1 | >=852 | >=10.7 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 247-279 | 31-25 |
| VMM4SH-N35SH | 1170-1240 | 11.7-12.4 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 263-295 | 33-37 |
| VMM5SH-N38SH | 1220-1290 | 12.2-12.9 | >=915 | >=11.5 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM6SH-N40SH | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=939 | >=11.8 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM7SH-N42SH | 1290-1350 | 12.9-13.5 | >=963 | >=12.1 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 318-350 | 40-44 |
| VMM8SH-N44SH | 1310-1370 | 13.1-13.7 | >=979 | >=12.3 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 326-358 | 41-45 |
| VMM9SH-N46SH | 1340-1400 | 13.4-14.0 | >=995 | >=12.5 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 342-374 | 43-47 |
| VMM10SH-N48SH | 1370-1430 | 13.7-14.3 | >=1011 | >=12.7 | >=1592 | >=20.0 | 358-390 | 45-49 |
| VMM UH - to 180 °C | ||||||||
| VMM3UH-N30UH | 1080-1160 | 10.8-11.6 | >=812 | >=10.2 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 223-255 | 28-32 |
| VMM4UH-N33UH | 1140-1210 | 11.4-12.1 | >=852 | >=10.7 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 247-276 | 31-35 |
| VMM5UH-N35UH | 1170-1240 | 11.7-12.4 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 263-295 | 33-37 |
| VMM6UH-N38UH | 1220-1290 | 12.2-12.9 | >=915 | >=11.5 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM7UH-N40UH | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=939 | >=11.8 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM8UH-42UH | 1290-1350 | 12.9-13.5 | >=963 | >=12.1 | >=1990 | >=25.0 | 318-350 | 40-44 |
| VMM EH - to 200 °C | ||||||||
| VMM3EH-N30EH | 1080-1150 | 10.8-11.5 | >=812 | >=10.2 | >=2388 | >=30.0 | 223-255 | 28-32 |
| VMM4EH-N33EH | 1140-1210 | 11.4-12.1 | >=852 | >=10.7 | >=2388 | >=30.0 | 247-279 | 31-35 |
| VMM5EH-N38EH | 1220-1290 | 12.2-12.9 | >=915 | >=11.5 | >=2388 | >=30.0 | 287-318 | 36-40 |
| VMM6EH-N40EH | 1260-1320 | 12.6-13.2 | >=939 | >=11.8 | >=2388 | >=30.0 | 302-334 | 38-42 |
| VMM AH - to 230 °C | ||||||||
| VMM3AH-N28AH | 1040-1120 | 10.4-11.2 | >=772 | >=9.7 | >=2786 | >=35.0 | 207-239 | 26-30 |
| VMM4AH-N30AH | 1080-1150 | 10.8-11.5 | >=812 | >=10.2 | >=2786 | >=35.0 | 223-255 | 28-32 |
| VMM5AH-N33AH | 1140-1210 | 11.4-12.1 | >=852 | >=10.7 | >=2786 | >=35.0 | 247-279 | 31-35 |
| VMM6AH-N35AH | 1170-1240 | 11.7-12.4 | >=876 | >=11.0 | >=2786 | >=35.0 | 263-295 | 33-37 |
1.0 Kgs=100 mT, 1.0 Koe=79.6KA/m, 1.0 MGOe=7.96 KJ/m3
Maximum working temperature (in close circuit)
| Typ | VMM 5 -12 | VMM 3M - 9M | VMM 4H - 11H | VMM 3SH - 10SH | VMM 3UH - 8UH | VMM 3EH - 6EH | VMM 3AH - 6AH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | do 80 | do 100 | do 120 | do 150 | do 180 | do 200 | do 230 |
Related magnets

Samarium-cobalt magnets SmCo

Ferrite magnets

Office magnets

Coated magnets

Clip magnets